- Specialities
- Laparoscopic Myomectomy
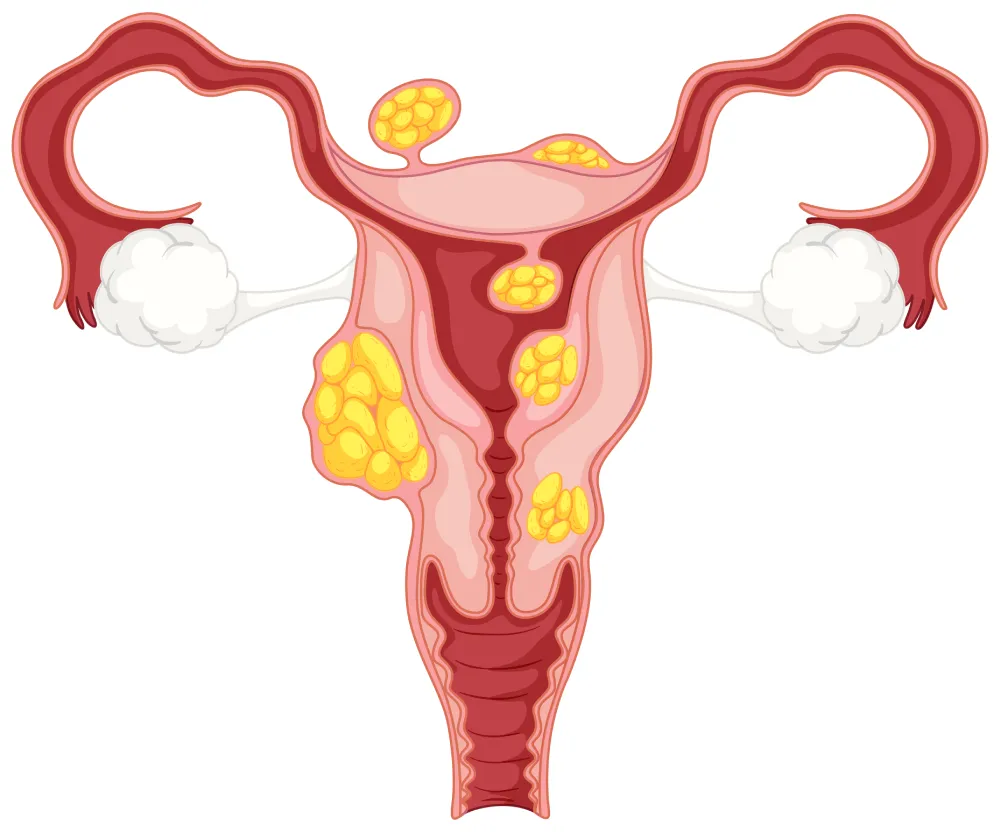
What is a Laparoscopic Myomectomy?
Myomectomy is a surgical process of removing uterine fibroids. Uterine fibroids are non-cancerous growth of the uterus. It occurs during the childbearing days or can be developed at any age. Myomectomy is best for women who want a baby in the future. Unlike hysterectomy (complete removal of the uterus), it only removes fibroids and leaves the uterus in place.
Types of Myomectomy
- Laparoscopic Myomectomy: Involves making a few small incisions in the abdomen to remove fibroids. The surgeon uses a laparoscope to view the uterus and guide the instruments.
- Hysteroscopic Myomectomy: Used for fibroids located inside the uterine cavity. A hysteroscope (a thin, lighted instrument) is inserted through the vagina and cervix into the uterus to remove the fibroids.
- Abdominal Myomectomy (Laparotomy): Involves a larger incision in the abdomen to remove fibroids, typically used for very large or numerous fibroids.
Symptoms Indicating the Need for a Myomectomy
Fibroids can cause a range of symptoms, depending on their size, number, and location within the uterus. Common symptoms include:
- Heavy Menstrual Bleeding: Unusually heavy or prolonged periods, often leading to anemia.
- Pelvic Pain: Persistent pain or pressure in the pelvis.
- Frequent Urination: Due to pressure on the bladder.
- Constipation: Fibroids pressing against the rectum can cause bowel issues.
- Pain During Intercourse: Depending on the location of the fibroids.
- Enlarged Uterus or Abdomen: Leading to a bloated appearance.
- Reproductive Issues: Infertility, recurrent miscarriages, or complications during pregnancy.
Benefits
- Preserving Fertility:Laparoscopic myomectomy can improve fertility and help women become pregnant after surgery. It is also an excellent option for women who wish to preserve their fertility for the future.
- Faster Recovery: This procedure typically results in less pain and blood loss compared to traditional abdominal myomectomies, allowing patients to recover within 1–2 weeks.
- Reduced Risk of Adhesions:Laparoscopic myomectomy leads to fewer adhesions (scar tissue) than traditional abdominal myomectomies.
- Improved Outcomes:This technique can result in better pregnancy outcomes, including a lower risk of uterine rupture during pregnancy and labor.